Explore All Articles
All Articles
Article Topic
Information control on YouTube during Russia’s invasion of Ukraine
Yevgeniy Golovchenko, Kristina Aleksandrovna Pedersen, Jonas Skjold Raaschou-Pedersen and Anna Rogers
This research note investigates the aftermath of YouTube’s global ban on Russian state-affiliated media channels in the wake of Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine in 2022. Using over 12 million YouTube comments across 40 Russian-language channels, we analyzed the effectiveness of the ban and the shifts in user activity before and after the platform’s intervention.
LLMs grooming or data voids? LLM-powered chatbot references to Kremlin disinformation reflect information gaps, not manipulation
Maxim Alyukov, Mykola Makhortykh, Alexandr Voronovici and Maryna Sydorova
Some of today’s most popular large language model (LLM)-powered chatbots occasionally reference Kremlin-linked disinformation websites, but it might not be for the reasons many fear. While some recent studies have claimed that Russian actors are “grooming” LLMs by flooding the web with disinformation, our small-scale analysis finds little evidence for this.

Stochastic lies: How LLM-powered chatbots deal with Russian disinformation about the war in Ukraine
Mykola Makhortykh, Maryna Sydorova, Ani Baghumyan, Victoria Vziatysheva and Elizaveta Kuznetsova
Research on digital misinformation has turned its attention to large language models (LLMs) and their handling of sensitive political topics. Through an AI audit, we analyze how three LLM-powered chatbots (Perplexity, Google Bard, and Bing Chat) generate content in response to the prompts linked to common Russian disinformation narratives about the war in Ukraine.

Search engine manipulation to spread pro-Kremlin propaganda
Evan M. Williams and Kathleen M. Carley
The Kremlin’s use of bots and trolls to manipulate the recommendation algorithms of social media platforms is well-documented by many journalists and researchers. However pro-Kremlin manipulation of search engine algorithms has rarely been explored. We examine pro-Kremlin attempts to manipulate search engine results by comparing backlink and keyphrase networks of US, European, and Russian think tanks, as well as Kremlin-linked “pseudo” think tanks that target Western audiences.

Mapping the website and mobile app audiences of Russia’s foreign communication outlets, RT and Sputnik, across 21 countries
Julia Kling, Florian Toepfl, Neil Thurman and Richard Fletcher
Following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, policymakers worldwide have taken measures to curb the reach of Russia’s foreign communication outlets, RT and Sputnik. Mapping the audiences of these outlets in 21 countries, we show that in the quarter before the invasion, at least via their official websites and mobile apps, neither outlet reached more than 5% of the digital populations of any of these countries each month.

Clarity for friends, confusion for foes: Russian vaccine propaganda in Ukraine and Serbia
Katrina Keegan
This paper examines how Russia tailors its vaccine propaganda to hostile and friendly audiences, like Ukraine and Serbia. Web scraping of all articles about vaccines on Russian state-owned websites from December 2020 to November 2021 provided data for quantitative topic modeling and qualitative analysis.

A story of (non)compliance, bias, and conspiracies: How Google and Yandex represented Smart Voting during the 2021 parliamentary elections in Russia
Mykola Makhortykh, Aleksandra Urman and Mariëlle Wijermars
On 3 September 2021, the Russian court forbade Google and Yandex to display search results for “Smart Voting,” the query referring to a tactical voting project by the jailed Russian opposition leader Alexei Navalny. To examine whether the two search engines complied with the court order, we collected top search outputs for the query from Google and Yandex.

Elections
Source alerts can reduce the harms of foreign disinformation
Jason Ross Arnold, Alexandra Reckendorf and Amanda L. Wintersieck
Social media companies have begun to use content-based alerts in their efforts to combat mis- and disinformation, including fact-check corrections and warnings of possible falsity, such as “This claim about election fraud is disputed.” Another harm reduction tool, source alerts, can be effective when a hidden foreign hand is known or suspected.
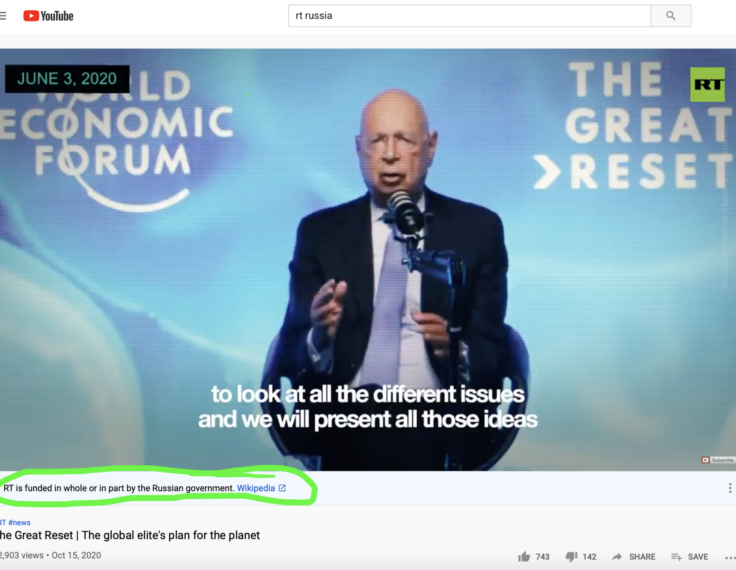
Elections
State media warning labels can counteract the effects of foreign misinformation
Jack Nassetta and Kimberly Gross
Platforms are increasingly using transparency, whether it be in the form of political advertising disclosures or a record of page name changes, to combat disinformation campaigns. In the case of state-controlled media outlets on YouTube, Facebook, and Twitter this has taken the form of labeling their connection to a state.
